ovirt-imageio
Daniel Erez - derez@redhat.com
Senior Software Engineer
June 2018
Agenda
-
Overview
-
Setup
-
WebAdmin
-
API
-
Random I/O
-
Error Handling
-
Logs
-
Documentation
-
Future Work
Overview
Goal: Uploading an Image to a Storage Domain



Overview
Goal: Downloading an Image from a Storage Domain



Overview
imageio modules
ovirt-imageio-proxy
A service that functions as a proxy server allowing clients, without access to the host network, to perform I/O operations on disks and snapshots located within the oVirt virtualization environment.
ovirt-imageio-daemon
A service that provides direct access to oVirt disks and snapshots using HTTPS protocol. Together with ovirt-imageio-proxy, it allows uploading/downloading disks directly into/from an oVirt disk (also, supporting random I/O).
ovirt-imageio-common
Common functionality for ovirt-imageio-daemon and ovirt-imageio-proxy (and virt-v2v in vdsm).
Overview
Step 1: Initiate transfer (upload/download)
using UI
UI
Backend
imageio-proxy
VDSM
imageio-daemon
Upload
TransferDiskImage
Transfer Type
(Upload/Download)
Transfer Size
Disk Parameters
AddDisk
AddImageTicket
PUT /tickets
Ticket UUID
Proxy Address +
Ticket UUID
Overview
Step 1: Initiate transfer (upload/download)
using API
API
Backend
imageio-proxy
VDSM
imageio-daemon
Upload
Create ImageTransfer
Disk ID
Transfer Type
(Upload/Download)
AddDisk
AddImageTicket
PUT /tickets
Proxy Address +
Ticket UUID
AddDisk
Overview
Step 2: Stream Data
UI/API
imageio-proxy
imageio-daemon
Upload
PUT /images/<ticket_uuid>
PUT /images/<ticket_uuid>

Stream
Download
GET /images/<ticket_uuid>
GET /images/<ticket_uuid>
Stream
Send Chunk
Get Chunk

Overview
Step 3: End Upload
UI/REST
Backend
imageio-proxy
VDSM
imageio-daemon
Finalize
TransferImageStatus
Finished
Teardown Image (cleanup)
DELETE /tickets/<uuid>
DELETE /tickets/<uuid>
Delete Ticket
Unlock Disk
Setup
Install 'Image I/O Proxy' in engine-setup
$ engine_setup
...
--== PRODUCT OPTIONS ==--
...
Configure Image I/O Proxy on this host? (Yes, No) [Yes]:
...ovirt-imageio-proxy service
- Make sure ovirt-imageio-proxy is installed on engine machine (should be included with ovirt-engine installation).
- Make sure the service is running.
Setup
Install ovirt-engine's CA certificate in browser
Chrome
Setup
Install ovirt-engine's CA certificate in browser
Firefox
WebAdmin
Disk Upload Drop-Down Menu
-
Start - initiate a new upload
-
Cancel - stop an ongoing upload (needed to remove a paused upload)
-
Pause - temporarily stop an upload
-
Resume - re-initiate an existing upload (with the same image)
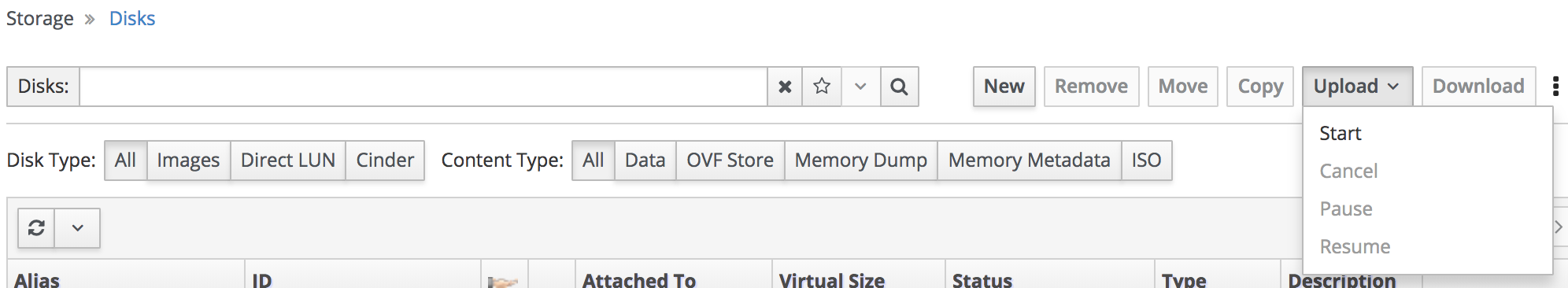
WebAdmin
Upload Image Dialog
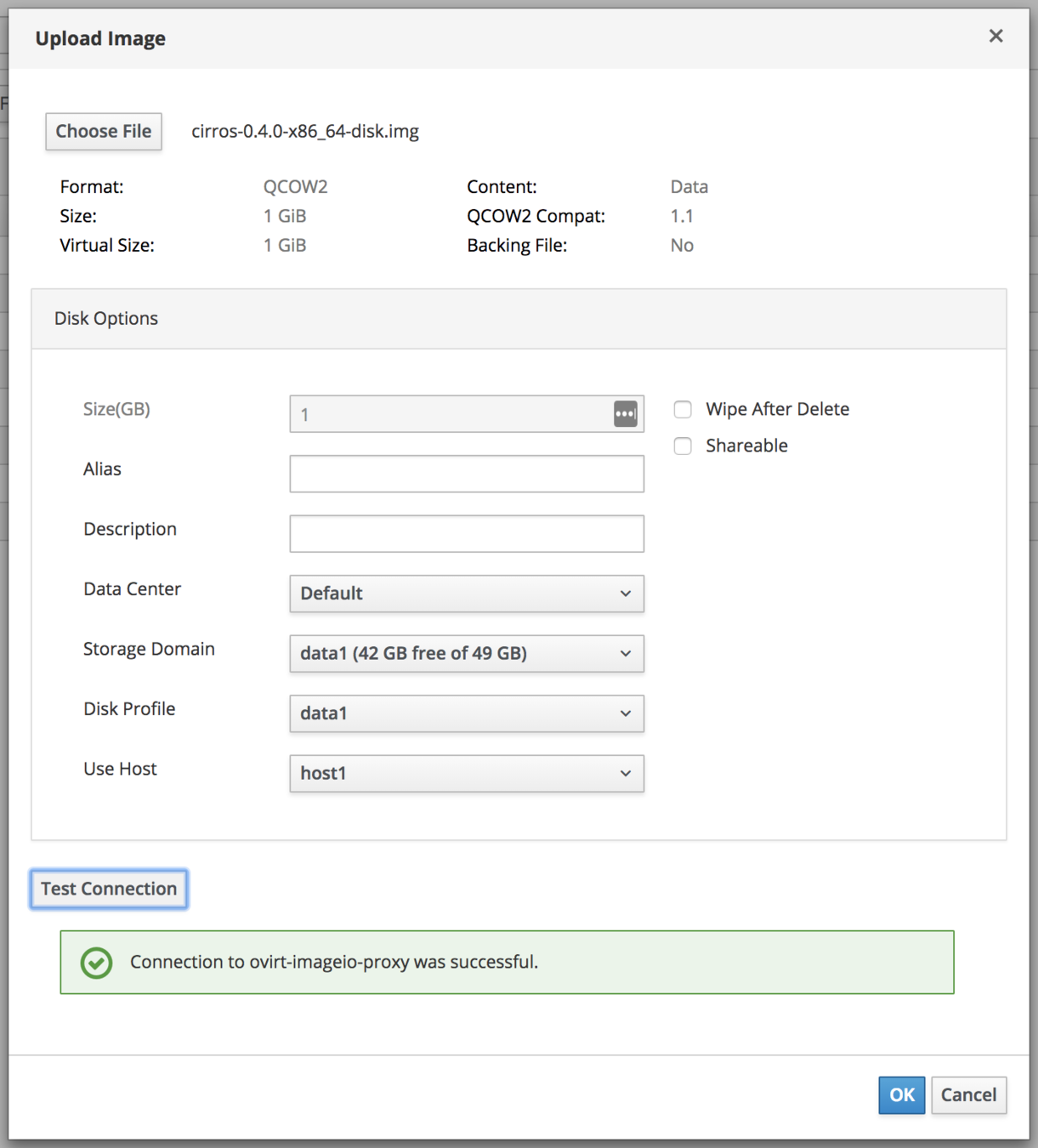
WebAdmin
Uploading...
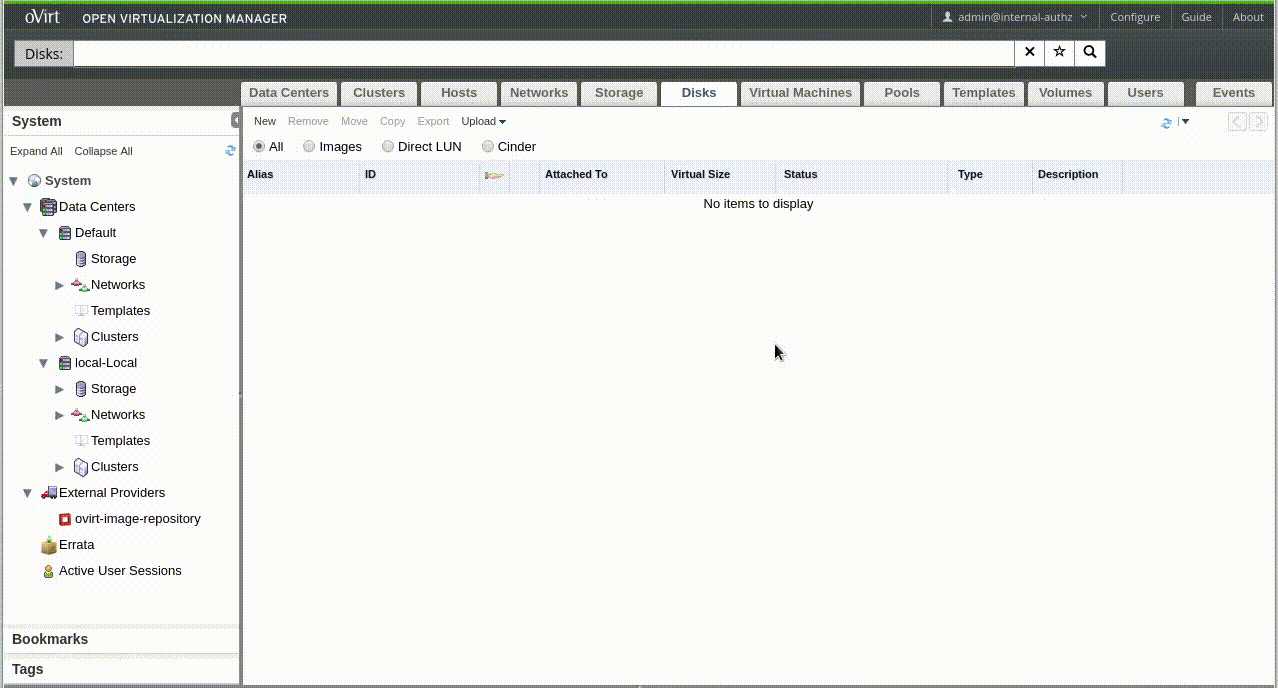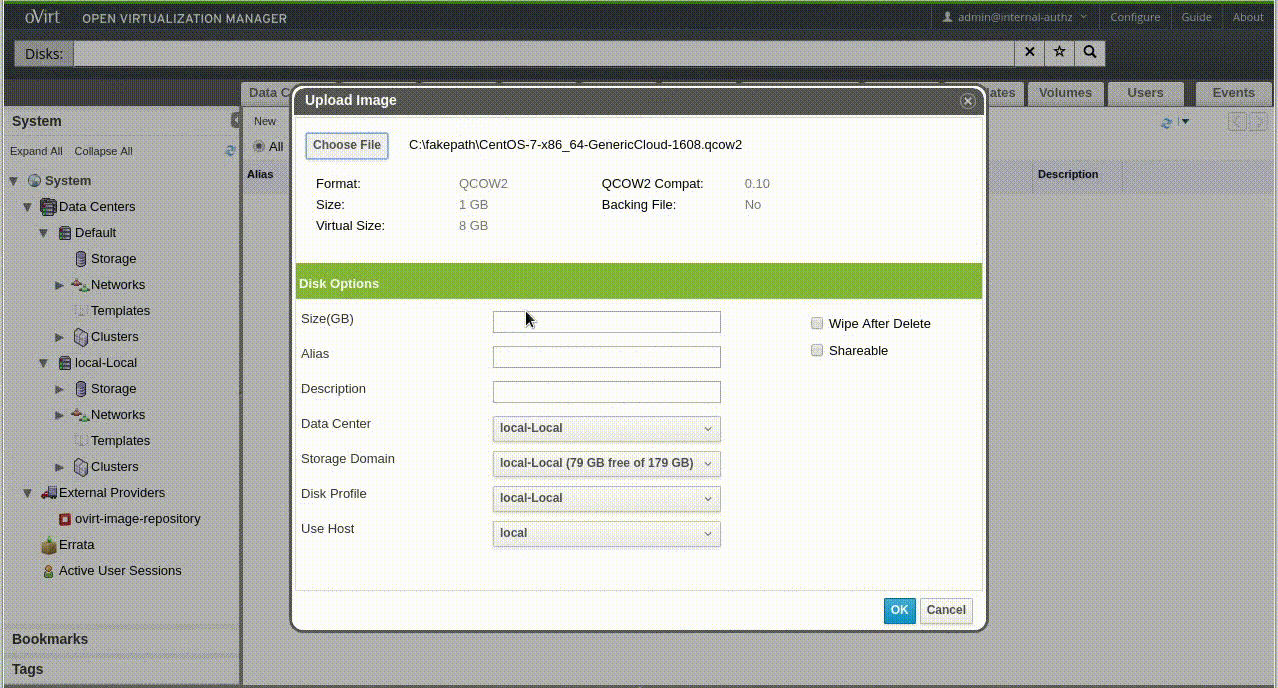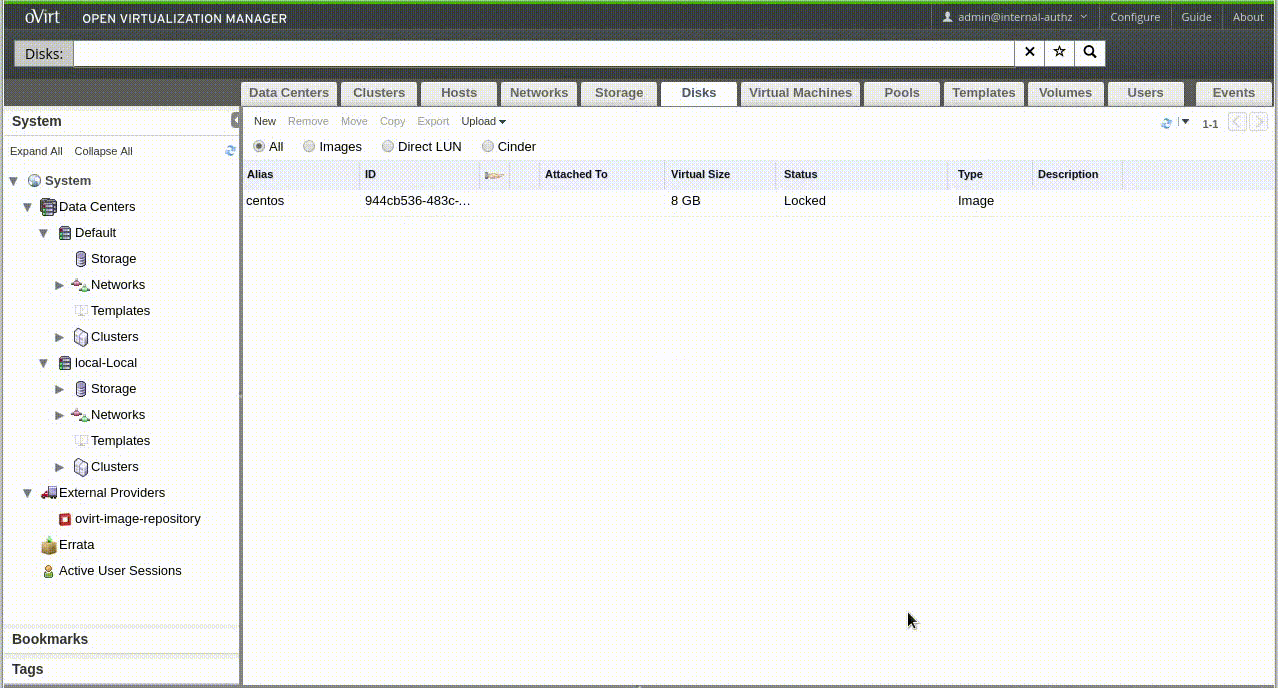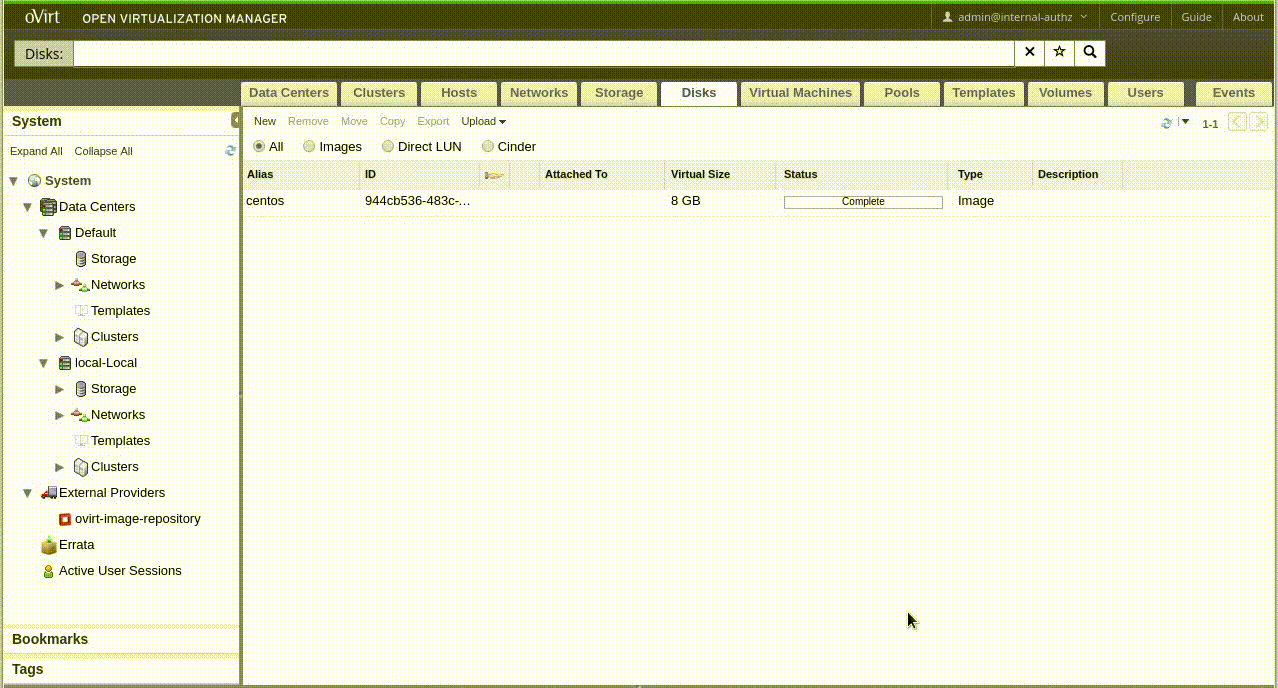
WebAdmin
Disk Download
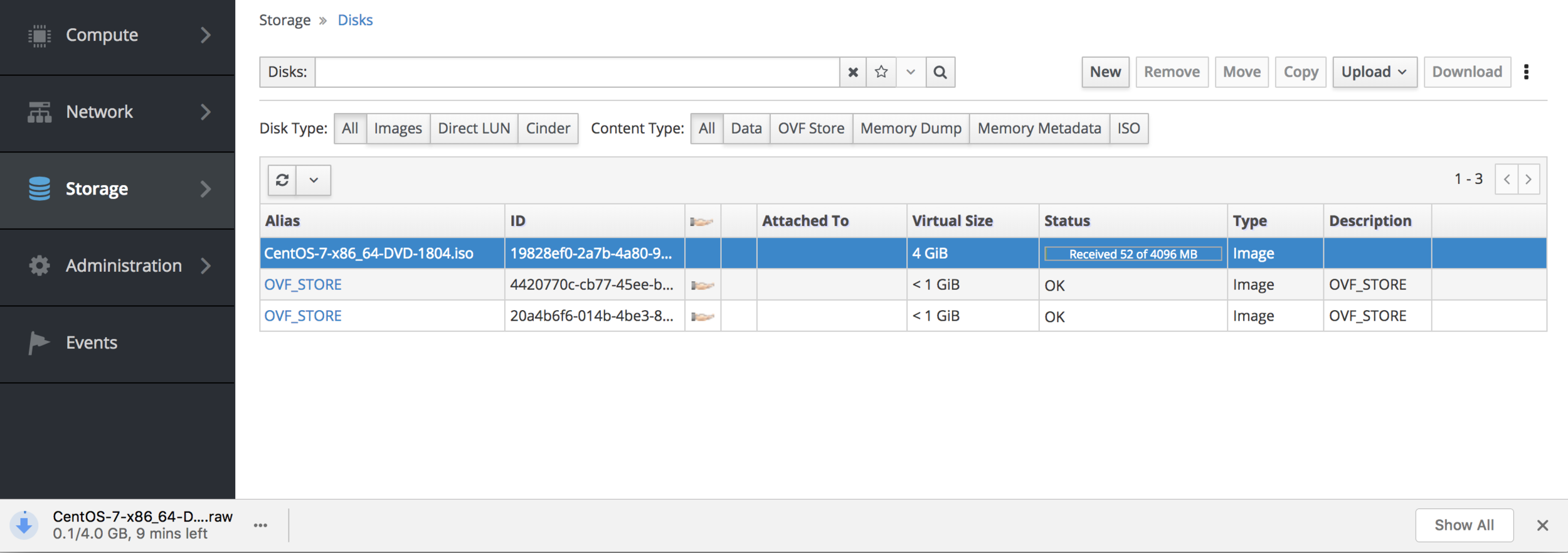
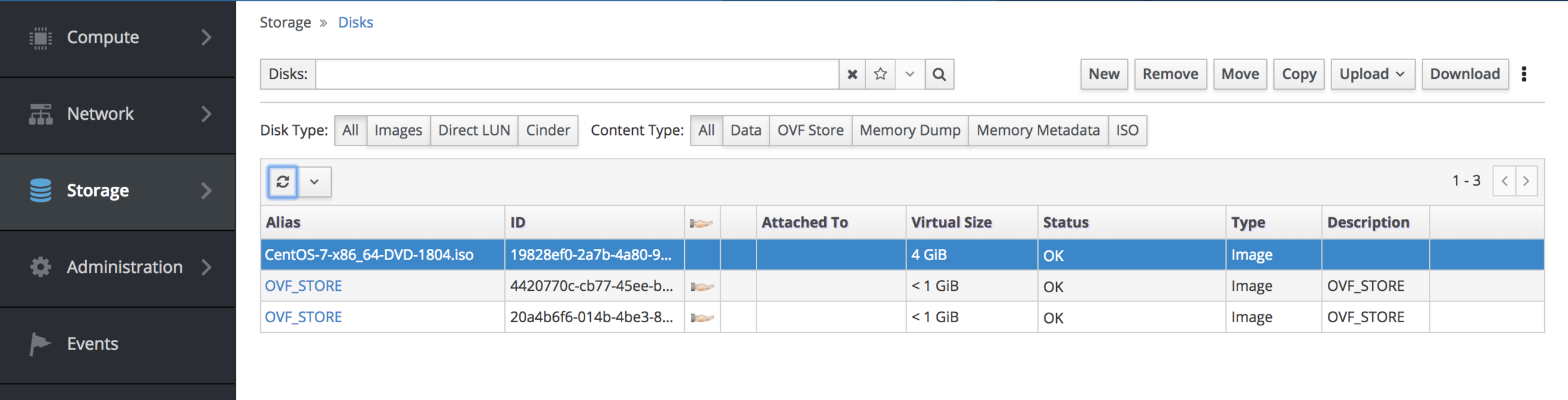
API
Examples in python-sdk:
More details in API documenation:
http://ovirt.github.io/ovirt-engine-api-model/master/#services/image_transfer
- Upload Disk:
https://github.com/oVirt/ovirt-engine-sdk/blob/master/sdk/examples/upload_disk.py - Download Disk:
https://github.com/oVirt/ovirt-engine-sdk/blob/master/sdk/examples/download_disk.py - Upload Disk Snapshot:
https://github.com/oVirt/ovirt-engine-sdk/blob/master/sdk/examples/upload_disk_snapshots.py - Download Disk Snapshots:
https://github.com/oVirt/ovirt-engine-sdk/blob/master/sdk/examples/download_disk_snapshots.py
API
disks_service = connection.system_service().disks_service()
disk = disks_service.add(
disk=types.Disk(
name='mydisk',
description='My disk',
format=types.DiskFormat.COW,
provisioned_size=1 * 2**30,
storage_domains=[
types.StorageDomain(
name='data',
),
],
)
)Step 1: Add a New Disk
disk_service = disks_service.disk_service(disk.id)
while True:
time.sleep(5)
disk = disk_service.get()
if disk.status == types.DiskStatus.OK:
break
Step 2: Wait till the disk is created
API
transfers_service = system_service.image_transfers_service()
transfer = transfers_service.add(
types.ImageTransfer(
disk=types.Image(id=disk.id),
-- or
snapshot=types.DiskSnapshot(id=disk_snapshot_id),
direction=types.ImageTransferDirection.UPLOAD/DOWNLOAD, [default: UPLOAD]
host=types.Host(id=host_id), [default: random host from DC]
inactivity_timeout=0, [default: 600]
)
)Step 3: Add a new image transfer
transfer_service = transfers_service.image_transfer_service(transfer.id)
while transfer.phase == types.ImageTransferPhase.INITIALIZING:
time.sleep(1)
transfer = transfer_service.get()Step 4: Wait until the init phase is over
API
destination_url = urlparse(transfer.proxy_url)
[use 'proxy_url' for transferring from/to ovirt-imageio-proxy]
-- or
destination_url = urlparse(transfer.transfer_url)
[use 'transfer_url' for transferring directly from/to ovirt-imageio-daemon]
context = ssl.create_default_context()
context.load_verify_locations(cafile='ca.pem')
connection = HTTPSConnection(
destination_url.hostname,
destination_url.port,
context=context,
)Step 5: Initiate connection
API
# Send the request header
image_size = os.path.getsize(path)
connection.putrequest("PUT", destination_url.path)
connection.putheader('Content-Length', "%d" % (image_size))
connection.endheaders()
# Send the request body
CHUNK_SIZE = 8 * 1024 * 1024
with open(path, "rb") as disk:
pos = 0
while pos < image_size:
# Send the next chunk to the proxy/daemon.
to_read = min(image_size - pos, CHUNK_SIZE)
chunk = disk.read(to_read)
if not chunk:
transfer_service.pause()
raise RuntimeError("Unexpected end of file at pos=%d" % pos)
connection.send(chunk)
pos += len(chunk)
now = time.time()
# Report progress every 10 seconds.
if now - last_progress > 10:
print("Uploaded %.2f%%" % (float(pos) / image_size * 100))
last_progress = nowStep 6: Stream Data
Random I/O
-
Introduced in oVirt 4.2
-
Required for use cases such as:
-
Resuming interrupted upload or download
-
Efficient upload of a sparse image
-
Integration with virt-v2v
-
-
Documentation:
http://ovirt.github.io/ovirt-imageio/random-io.html
Random I/O
Resuming incomplete download
Client (browser/curl/etc) sends "Range" header in the GET request.
Usages
E.g.
GET /images/TICKET-ID
Range: bytes=START-ENDE.g.
PUT /images/TICKET-ID
Content-Range: bytes START-END/LENGTHResuming incomplete upload
Client (browser/curl/etc) sends "Content-Range" header in the PUT request.
Random I/O
Zero
Zero a byte range without sending the actual zeros over the wire.
Operations
PATCH /images/TICKET-ID
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: LENGTH
{
"op": "zero",
"offset": 4096,
"size": 8192,
"flush": false [if true: flush data to storage before responding]
}
Flush
Flush the data written to the image to the underlying storage. The call returns only when the device reports that the transfer was done.
PATCH /images/TICKET-ID
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: LENGTH
{
"op": "flush"
}Random I/O
Describes the available methods for a resource.
Options
OPTIONS /images/ticket_id HTTP/1.1Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Allow: GET,PUT,PATCH,OPTIONS
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: LENGTH
{
"features": ["zero", "flush"]
}Request:
Error Handling
Symptom: test connection to proxy failed
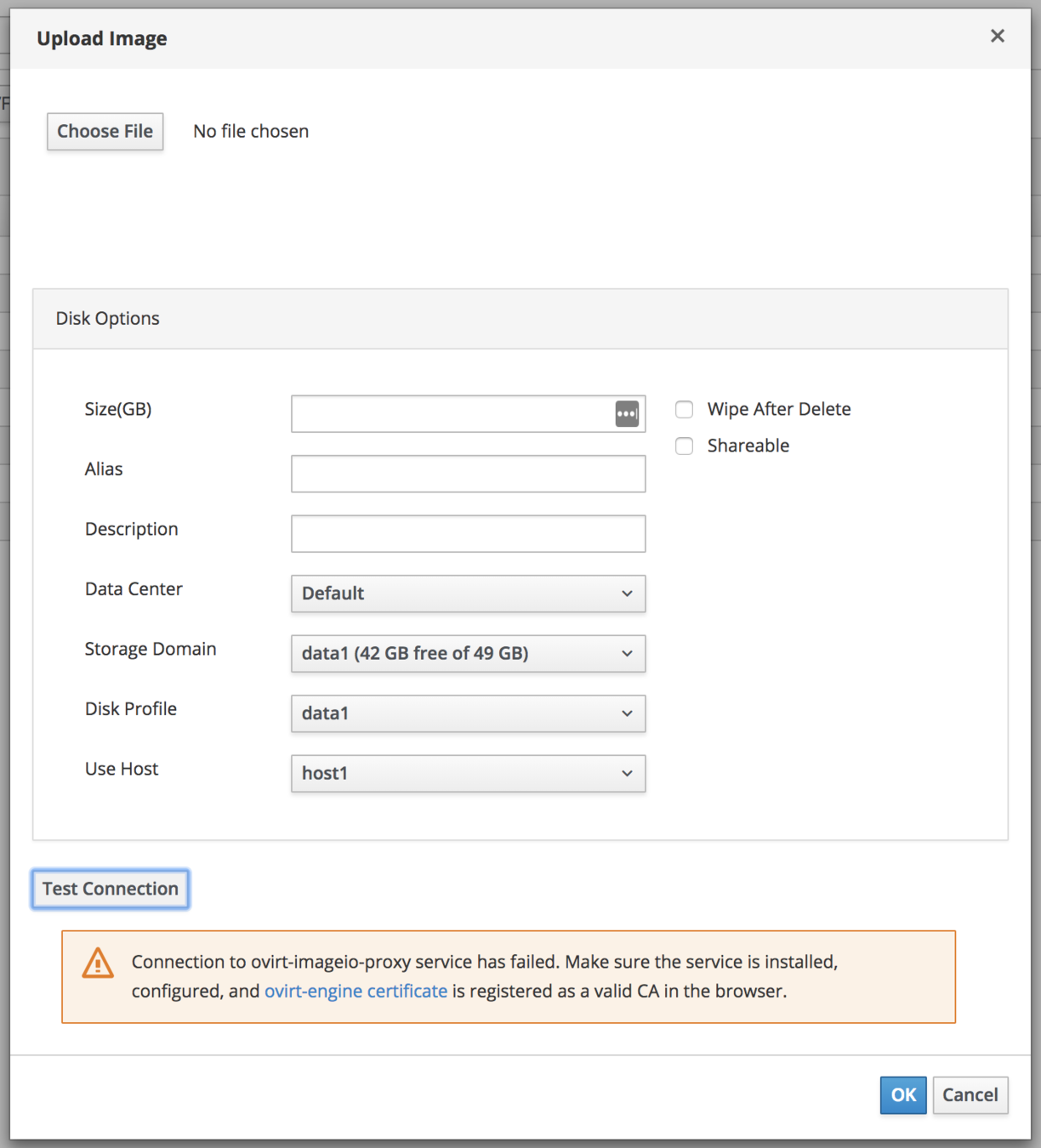
Error Handling
Resolution:
- Import the certificate using the 'ovirt-engine certificate' link and restart the browser. A green lock should appear in the address bar:
- Make sure ovirt-imageio-proxy service is installed and running (in engine machine).
- Check ImageProxyAddress configuration value with engine-config:
# engine-config -g ImageProxyAddress
Should be 'engine-hostname:proxy-port', e.g. engine:54323
Error Handling
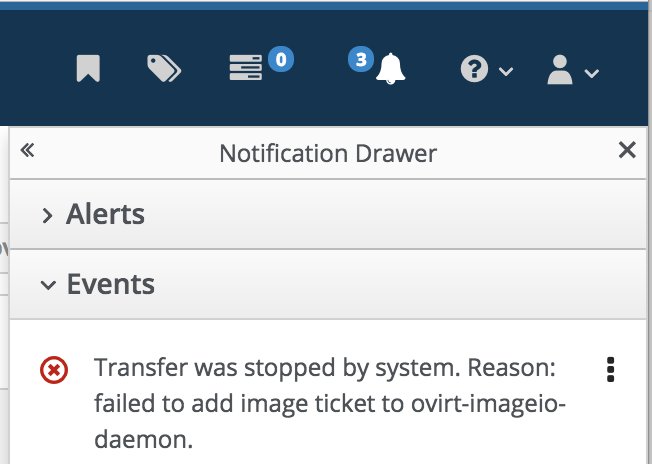
Symptom: 'Paused By System' status
Resolution:
- Use 'Test Connection' button in upload disk dialog to ensure connectivity between WebAdmin to the proxy.
- Ensure ovirt-imageio-daemon service is running (in the host).
- Look in the events tab for more information, e.g.

Logs
/var/log/ovirt-imageio-proxy/image-proxy.logovirt-image-proxy service - in engine machine
/var/log/ovirt-imageio-daemon/daemon.logovirt-image-daemon service - in host (vdsm) machine
Console tab in browser's Developer Tools
Documentation
- Project in GitHub:
https://github.com/oVirt/ovirt-imageio - GitHub Pages Site:
http://ovirt.github.io/ovirt-imageio - API:
http://ovirt.github.io/ovirt-engine-api-model/master/#services/image_transfer - python SDK examples:
https://github.com/oVirt/ovirt-engine-sdk/blob/master/sdk/examples/ - Feature Page:
https://www.ovirt.org/develop/release-management/features/storage/image-upload/
Future Work
-
unix socket support (planned for 4.2.z)
-
Eliminates the overhead of reading from SSL socket
(which is our bottleneck when using fast storage)
-
-
Use concurrent I/O for upload
-
Improves throughput.
-
-
Integration with an NBD (network block device) server
-
High performance (e.g. parallel requests)
-
Efficient handling of different storage types
-
-
Sparseness support - smart uploading of sparse image, without the zero 'holes' (using 'qemu-img map' and random I/O support).
-
Incremental Backup - integrating CBT (Changed Block Tracking) support introduced in qemu.